- Fitwell Physiotherapy
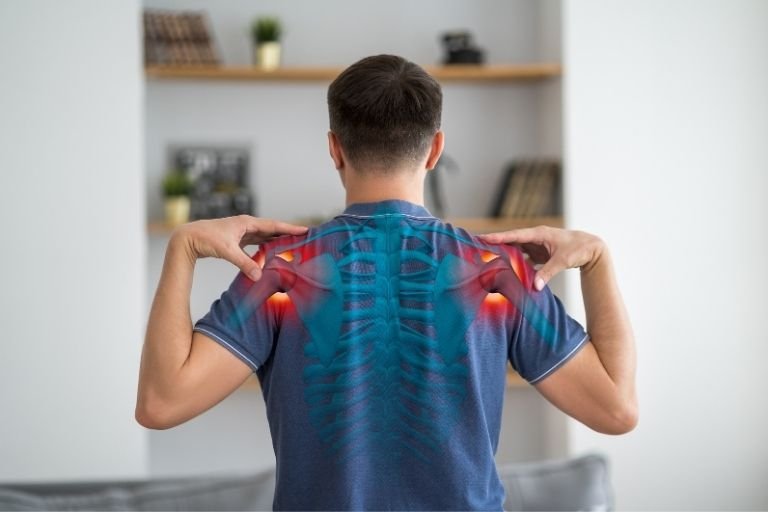
Shoulder Fracture

A shoulder fracture can be a painful and debilitating injury, impacting your ability to perform everyday tasks and participate in physical activities. Let’s delve into the symptoms, causes, when to seek a physiotherapist, risks, prevention strategies, and treatments associated with shoulder fractures.
Please submit your details below.
Symptoms:
- Pain: Severe pain in the shoulder area, particularly upon movement.
- Swelling: Swelling and tenderness around the shoulder joint.
- Bruising: Visible bruising or discoloration around the affected area.
- Limited Range of Motion: Difficulty moving the shoulder joint, especially lifting or rotating the arm.
- Deformity: In severe cases, the shoulder may appear deformed or misshapen.
Causes:
- Trauma: The most common cause of shoulder fractures is trauma, such as a fall onto an outstretched arm or a direct blow to the shoulder.
- Sports Injuries: Participating in contact sports or activities that involve repetitive overhead movements can increase the risk of shoulder fractures.
- Osteoporosis: Weakened bones due to conditions like osteoporosis can make the shoulder more susceptible to fractures, even from minor trauma.
When to See a Physiotherapist:
It’s essential to seek medical attention promptly if you suspect a shoulder fracture. A physiotherapist can assess the extent of the injury, provide pain management strategies, and develop a tailored rehabilitation plan to facilitate recovery. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe pain, swelling, or difficulty moving your shoulder.
Risks:
- Chronic Pain: Without proper treatment and rehabilitation, a shoulder fracture can lead to chronic pain and stiffness.
- Loss of Function: Untreated fractures or inadequate rehabilitation can result in decreased shoulder mobility and function.
- Complications: In some cases, shoulder fractures can lead to complications such as nerve damage or arthritis if not managed effectively.
Prevention:
- Strengthening Exercises: Engage in regular shoulder-strengthening exercises to improve muscle strength and stability, reducing the risk of fractures.
- Proper Technique: Practice proper techniques when participating in sports or activities to minimize the risk of injury.
- Fall Prevention: Take precautions to prevent falls, such as keeping walkways clear of obstacles and using handrails on stairs, especially for individuals at risk of osteoporosis.
Treatments:
- Immobilization: Depending on the severity of the fracture, immobilization with a sling or brace may be necessary to allow the bone to heal properly.
- Physiotherapy: Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in shoulder fracture recovery, focusing on exercises to improve range of motion, strength, and flexibility.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain medications or prescription pain relievers may be prescribed to manage pain during the healing process.
- Surgery: In severe cases or if the fracture is displaced, surgical intervention may be required to realign the bones and stabilize the shoulder joint.
In conclusion, shoulder fractures can significantly impact your quality of life, but with prompt medical attention, appropriate rehabilitation, and preventive measures, you can facilitate recovery and reduce the risk of future injuries. If you suspect a shoulder fracture, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and treatment.