- Fitwell Physiotherapy
Rheumatoid Arthritis

Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by inflammation of the joints, which can lead to pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased mobility. It primarily affects the synovium, the lining of the joints, but can also impact other organs such as the heart, lungs, and skin.
Please submit your details below.
Symptoms:
- Joint Pain and Stiffness: Typically more pronounced in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
- Swelling and Warmth: Joints may become swollen, tender, and warm to the touch.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness and lack of energy, often associated with RA flare-ups.
- Reduced Range of Motion: Difficulty moving joints through their full range of motion due to inflammation and joint damage.
- Systemic Symptoms: In some cases, RA can lead to fever, weight loss, and anemia.
Causes:
The exact cause of rheumatoid arthritis is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors. The immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues, primarily targeting the synovium. This immune response leads to inflammation, joint damage, and other systemic effects.
When to See a Physiotherapist:
It’s important to consult a physiotherapist if you experience:
- Persistent joint pain or stiffness
- Difficulty performing daily activities due to joint symptoms
- Decreased range of motion or muscle weakness
- Newly diagnosed RA or experiencing a flare-up
Risks:
If left untreated, rheumatoid arthritis can lead to:
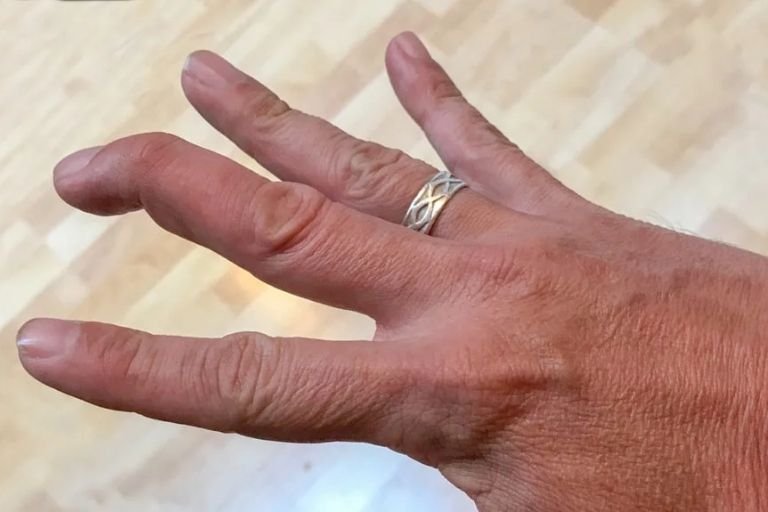
- Joint Damage: Chronic inflammation can cause cartilage and bone destruction, leading to deformities and disability.
- Cardiovascular Complications: RA increases the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Reduced Quality of Life: Pain, fatigue, and physical limitations can significantly impact daily activities and emotional well-being.
Prevention:
While there’s no surefire way to prevent RA, certain lifestyle changes may help reduce the risk or severity of symptoms:
- Regular Exercise: Maintain a balanced exercise routine to strengthen muscles, improve joint flexibility, and manage weight.
- Healthy Diet: Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids to reduce inflammation.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking increases the risk of developing RA and can worsen symptoms.
Treatments:
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biologic agents are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and slow disease progression.
- Physiotherapy: Tailored exercise programs, manual therapy, and assistive devices can help manage pain, improve joint function, and enhance mobility.
- Occupational Therapy: Techniques and devices to ease daily tasks and prevent joint strain.
- Surgery: In severe cases, joint replacement surgery may be necessary to relieve pain and restore function.
Conclusion:
Rheumatoid arthritis is a complex condition that requires a multidisciplinary approach for effective management. Early diagnosis, combined with appropriate medical treatment and lifestyle modifications, can help individuals with RA lead fulfilling lives with minimal joint damage and disability. Regular monitoring and communication with healthcare providers are essential for optimizing treatment outcomes and maintaining overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
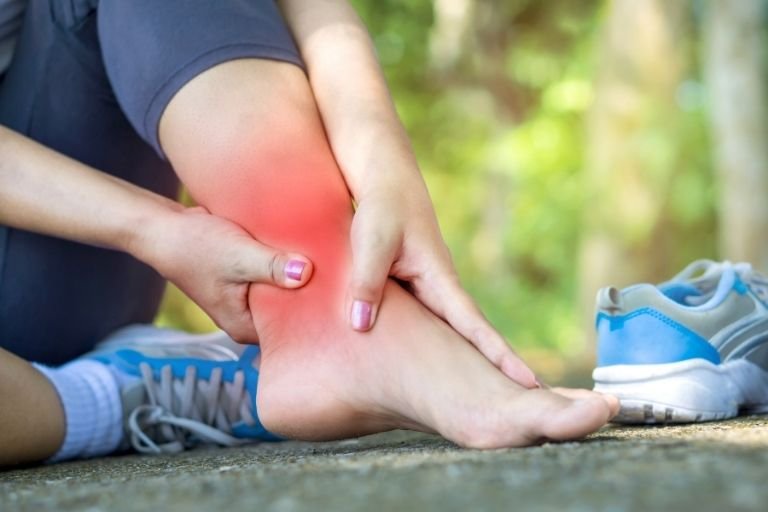
Recovery time can vary depending on factors such as the severity of the rupture, treatment approach, and individual healing capacity. Typically, recovery may take anywhere from 4 to 12 months. However, full return to pre-injury activities may take longer.
Treatment options include both surgical and non-surgical approaches. Non-surgical treatment may involve immobilization with a cast or walking boot, followed by physical therapy. Surgical repair may be recommended for younger, active individuals or severe ruptures, involving reattaching the torn tendon ends surgically.
Rehabilitation typically involves a progressive program focused on restoring strength, flexibility, and function of the affected leg. Initially, emphasis may be on protecting the healing tendon, followed by exercises to improve range of motion, strength, and eventually, functional activities such as walking and running.
While it’s not always possible to prevent all injuries, certain measures can reduce the risk of re-injury. These may include following a structured rehabilitation program, gradually returning to physical activities, wearing appropriate footwear, and incorporating exercises to strengthen the calf muscles and improve ankle stability.
Returning to sports or physical activities should be gradual and guided by your healthcare provider or physical therapist. Typically, athletes may start with low-impact activities such as swimming or cycling before progressing to higher-impact sports. The timing of return will depend on factors such as healing progress, strength, flexibility, and functional ability. It’s essential to avoid rushing the return to sports to minimize the risk of re-injury.
Related Conditions
How Fitwell Physiotherapy Can Help?
Dr. Richa’s Fitwell physiotherapy has an extensive team of physiotherapists all within their own specialist areas of physiotherapy. Whatever your condition, we guarantee that we will have the best physiotherapist for you. We assess, diagnose, plan, cure and care for you.
Fitwell Physiotherapy Clinic, Pune provides you best physiotherapy treatment in Kharadi, pune. We also serve Chandan Nagar, Vadgaon Sheri, Keshav Nagar, Wagholi & nearby Areas in Pune. We are experts in treating Neck Pain, Hand Pain, Back Pain, Lower Back Pain, Knee Pain, Stiff Neck, Sciatica, Arthritis, Stroke Paralysis & Post Surgical Rehab.
We provide Specialized physiotherapy treatments in Sports Injuries, Pre and post Surgery, Neurologic, Pediatric, Chronic Pain/Fatigue, Rheumatology, Women’s Health, Men’s Health, Ergonomics, Vestibular, Amputees & all sort of Pain treatment and lifestyle conditions.