- Fitwell Physiotherapy
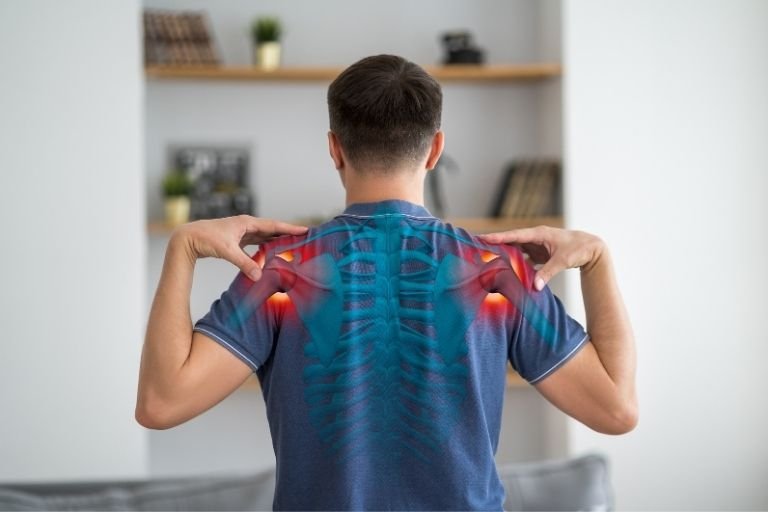
Acromio-Clavicular Joint Injury

The acromioclavicular joint (AC joint) injury is a common occurrence, especially among athletes participating in contact sports or those involved in activities with high impact on the shoulder area. This joint is located at the top of the shoulder, where the collarbone (clavicle) meets the highest point of the shoulder blade (acromion). When this joint is injured, it can cause significant discomfort and limit mobility in the shoulder region. Let’s delve into the details of AC joint injuries:
Please submit your details below.
Symptoms:
- Pain and tenderness around the top of the shoulder, specifically where the collarbone meets the shoulder blade.
- Swelling and inflammation in the affected area.
- Limited range of motion in the shoulder joint, especially when raising the arm overhead.
- A popping or clicking sensation with movement.
- Visible deformity or a bump above the shoulder joint in severe cases.
Causes:
- AC joint injuries commonly occur due to a sudden impact or trauma to the shoulder area, such as a fall onto an outstretched hand, a direct blow to the shoulder, or a collision during sports activities.
- Overuse or repetitive strain on the shoulder joint, particularly in athletes involved in activities like weightlifting, swimming, or overhead throwing sports.
When to See a Physiotherapist:
- If you experience persistent shoulder pain, swelling, or difficulty moving your arm after an injury.
- If you notice any deformity or abnormal bump above the shoulder joint.
- If the symptoms worsen or do not improve with rest and self-care measures.
Risks:
- Without proper treatment and rehabilitation, AC joint injuries can lead to chronic shoulder instability and long-term pain.
- Ignoring symptoms or returning to activities too soon can increase the risk of recurrent injuries and further damage to the shoulder joint.
How to Prevent:
- Strengthening exercises targeting the muscles around the shoulder joint can help improve stability and reduce the risk of injury.
- Proper warm-up and stretching before engaging in physical activities can help prepare the shoulder muscles and joints for movement.
- Using protective gear, such as shoulder pads or braces, during contact sports or activities with a high risk of shoulder injury.
- Avoiding overloading the shoulder joint with excessive weight or repetitive stress.
Treatments:
- Rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) can help reduce pain and inflammation in the early stages of injury.
- Physiotherapy exercises focusing on strengthening the shoulder muscles, improving flexibility, and restoring range of motion.
- Immobilization with a sling or brace to stabilize the shoulder joint during the healing process, especially for moderate to severe injuries.
- In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be recommended to alleviate pain and inflammation.
- Surgical intervention may be necessary for severe AC joint injuries or cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief.
Overall, prompt diagnosis and appropriate management are essential for recovering from an AC joint injury and preventing long-term complications. Seeking guidance from a physiotherapist or healthcare professional can help facilitate a safe and effective rehabilitation process tailored to your specific needs and goals.