Why Choose Us?
Working Hours
MON
10:00 – 13:00
17:00 – 20:00
TUE
10:00 – 13:00
17:00 – 20:00
WED
10:00 – 13:00
17:00 – 20:00
THU
10:00 – 13:00
17:00 – 20:00
FRI
10:00 – 13:00
17:00 – 20:00
SAT
10:00 – 13:00
17:00 – 20:00
SUN
10:00 – 13:00
17:00 – 20:00
Services

Expertise
Personalized Care

Comprehensive Services

Advance Treatment Techniques
Holistic Approach

Results-Oriented Approach
Our Services

Orthopaedic Physiotherapy
Orthopedic physiotherapy integrates specialized exercises, manual therapy, and education to alleviate pain, enhance mobility.

Neurological Physiotherapy
Neurological physiotherapy specializes in rehabilitating individuals with neurological conditions like stroke, Parkinson’s disease, spinal cord injuries, focusing on restoring function and independence.
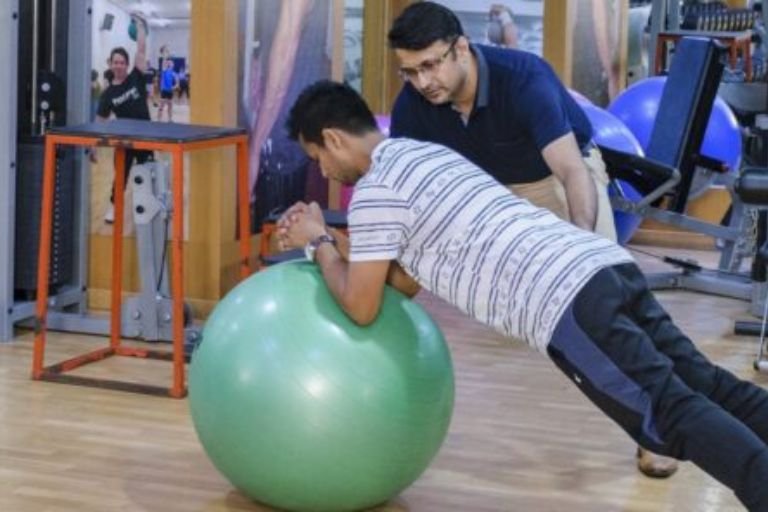

Sports & Fitness Physiotherapy
Sport and fitness physiotherapy encompasses injuryprevention,rehabilitation, performance enhancement for athletes and fitness enthusiasts, optimizing movement and promoting overall well-being.
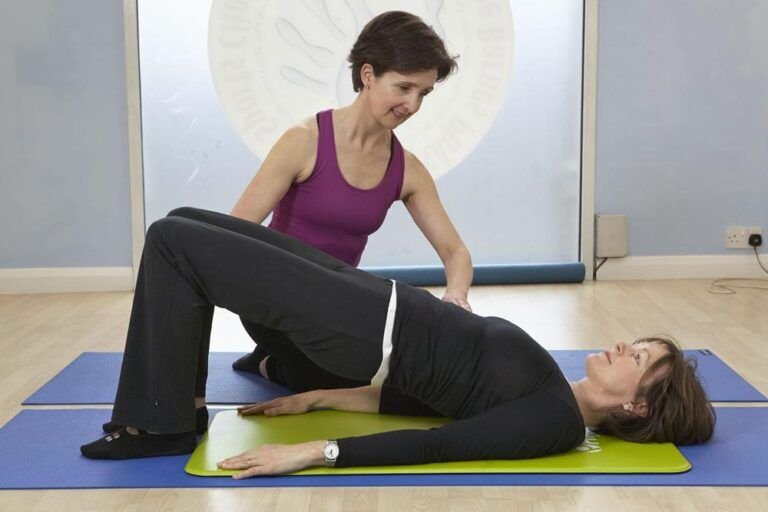

Women's Health Physiotherapy
Women’s health physiotherapy encompasses pelvic floor rehabilitation, prenatal ,postnatal care, and management of musculoskeletal issues, supporting women’s health

Ergonomics
Physiotherapists use ergonomics to improve work conditions, reducing strain and preventing injuries through proper posture, equipment adjustment, and movement techniques.
Pediatric Physiotherapy
Pediatrics physiotherapy is a specialized branch of physiotherapy focused on assessing, diagnosing, and treating physical and developmental disorders in infants, children, and adolescents.
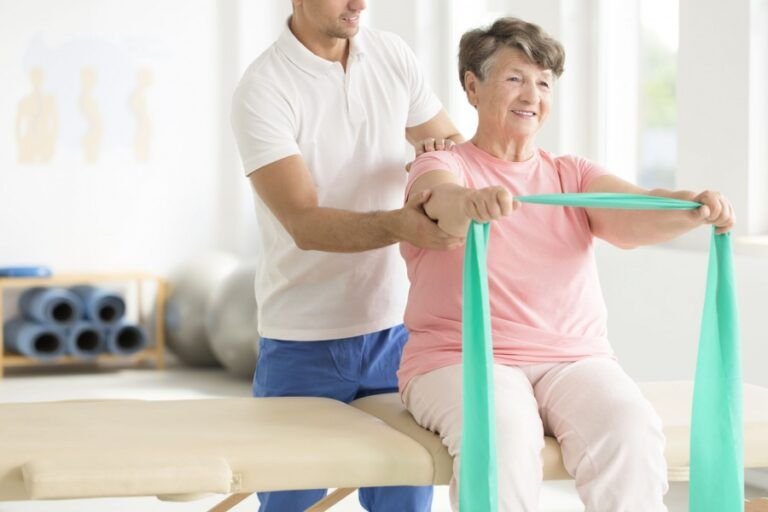

Geriatric Physiotherapy
Geriatric physiotherapy focuses on improving mobility, strength, and independence in older adults, addressing age-related conditions and promoting healthy aging.
Our Facilities

Car parking available for patients

Wheelchair assistance available

Full sanitisation done after each visit

Washrooms for male & female

Cash/UPI payment accepted

Video consultation available

Patient lift available

Home Visit Facility
Better Care for Better Quality of Life
In our clinic, we prioritize holistic care, recognizing that each individual is unique and requires personalized attention. Our approach goes beyond just treating symptoms; we focus on identifying and addressing the underlying causes of your condition to promote long-lasting results.
From manual therapy and exercise prescription to modalities like ultrasound, electrical stimulation, TENS, IFT, Traction and the most advance and successful method of TECAR Therapy we offer a comprehensive range of treatments to address a variety of musculoskeletal and neurological conditions.
Our goal is not only to treat your symptoms but also to empower you with the knowledge and tools you need to prevent future injuries and maintain your health long-term. So whether you’re recovering from surgery, managing a sports injury, looking for neuro rehab programme, having pelvic floor dysfunctions, posture related issues ,ergonomic advice,or simply looking to improve your mobility and function, we’re here to support you every step of the way. Our team of experienced physiotherapist are here to support you on your journey to recovery and improved function.
In our clinic, you’ll find a warm and welcoming environment designed to make you feel comfortable and at ease from the moment you walk in. Our friendly staff is dedicated to providing compassionate care and personalized attention to every patient who walks through our doors., we’re here to help you achieve your goals and live your best life.
Let us guide you regain confidence, restore function, and live life to the fullest.
Please submit your details below.

Latest Posts
Celebrating the Inauguration of Fitwell Physiotherapy Kharadi with Empowering Women
Celebrating Two Years of Success in Pelvic Floor Rehab and the July 2024 Progressive Kegels Exercise Protocol Learning Workshop
Corporate Ergonomic Session at WTC, Kharadi: A Moment of Pride and Joy
Client's Reviews


 Anil Naphade2024-03-06
Anil Naphade2024-03-06 I was looking for physiotherapist for the treatment of my frozen shoulders in KHARADI area close to my residence at Forest county . I came across Fitwell physiotherapy center and I am happy to share my experience. Dr Richa is expert in her field and after getting the treatment I got a relief in movement of my shoulder as original. She recommends only reasonable treatment . Overall very much satisfied with her treatment.
I was looking for physiotherapist for the treatment of my frozen shoulders in KHARADI area close to my residence at Forest county . I came across Fitwell physiotherapy center and I am happy to share my experience. Dr Richa is expert in her field and after getting the treatment I got a relief in movement of my shoulder as original. She recommends only reasonable treatment . Overall very much satisfied with her treatment.
 Sumit Dere2024-03-02
Sumit Dere2024-03-02 My chronic neck pain relieves after 8 sessions. Highly recommended
My chronic neck pain relieves after 8 sessions. Highly recommended
 Dwarkesh R2024-03-01
Dwarkesh R2024-03-01 I took several sessions with Dr Richa for addressing lower back pain post spine surgery that I had underwent. She is committed to providing the best care possible to her patients. I felt several improvements over the course of the treatment. Wish I had consulted her earlier :)
I took several sessions with Dr Richa for addressing lower back pain post spine surgery that I had underwent. She is committed to providing the best care possible to her patients. I felt several improvements over the course of the treatment. Wish I had consulted her earlier :)
 monika vashishtha2024-02-21
monika vashishtha2024-02-21 Dr. Richa is amazing, i had problem in my wrist from a very long time after visiting many doctors there was only short term relief. After visting her, i haven't had any issues in past 6-7 months. Dr richa really helped me.
Dr. Richa is amazing, i had problem in my wrist from a very long time after visiting many doctors there was only short term relief. After visting her, i haven't had any issues in past 6-7 months. Dr richa really helped me.
 priyamvada sinha2024-02-12
priyamvada sinha2024-02-12 I am writing to express my utmost satisfaction and gratitude for the exceptional care and service I received from Richa Purohit during my physiotherapy treatment at your clinic. I wanted to take a moment to share my positive experience with others. I initially sought Richa's assistance at a time when my pain levels were particularly challenging. From the moment I walked through the door, Richa extended a friendly and warm welcome that immediately put me at ease. What truly set her apart was her considerate inquiry before our first meeting, where she asked about my ability to walk stairs, as your office is located on the 1st floor. This level of consideration for my comfort and accessibility was something I had never experienced before. Richa's unique approach to treatment distinguished her from my previous experiences with other therapists. Her personalized care and attention to detail made a significant impact on my recovery journey. I appreciate her commitment to tailoring the treatment to individual needs, and it was evident that she genuinely cared about my well-being. I have since referred someone to Richa, confident that they will receive the same level of exceptional care that I did. I believe that her skills, compassion, and thoughtful approach make her a standout physiotherapist. In conclusion, I highly recommend Richa Purohit to anyone seeking professional and considerate physiotherapy care. Her expertise and genuine concern for her patients make her an asset to your clinic. Thank you for providing such a positive experience, and please extend my gratitude to Richa.
I am writing to express my utmost satisfaction and gratitude for the exceptional care and service I received from Richa Purohit during my physiotherapy treatment at your clinic. I wanted to take a moment to share my positive experience with others. I initially sought Richa's assistance at a time when my pain levels were particularly challenging. From the moment I walked through the door, Richa extended a friendly and warm welcome that immediately put me at ease. What truly set her apart was her considerate inquiry before our first meeting, where she asked about my ability to walk stairs, as your office is located on the 1st floor. This level of consideration for my comfort and accessibility was something I had never experienced before. Richa's unique approach to treatment distinguished her from my previous experiences with other therapists. Her personalized care and attention to detail made a significant impact on my recovery journey. I appreciate her commitment to tailoring the treatment to individual needs, and it was evident that she genuinely cared about my well-being. I have since referred someone to Richa, confident that they will receive the same level of exceptional care that I did. I believe that her skills, compassion, and thoughtful approach make her a standout physiotherapist. In conclusion, I highly recommend Richa Purohit to anyone seeking professional and considerate physiotherapy care. Her expertise and genuine concern for her patients make her an asset to your clinic. Thank you for providing such a positive experience, and please extend my gratitude to Richa.
 samriddhi tiwari2024-02-06
samriddhi tiwari2024-02-06 It was a wonderful experience with Dr. Richa she is highly professional and polite. I am grateful to have a support during physio sessions and even after that. She is one of the finest doctor for Physiotherapy and highly recommend her.
It was a wonderful experience with Dr. Richa she is highly professional and polite. I am grateful to have a support during physio sessions and even after that. She is one of the finest doctor for Physiotherapy and highly recommend her.
 Sudhanshu Rathore2023-07-22
Sudhanshu Rathore2023-07-22 Dr Richa is a very Polite and Knowledgeable doctor. She diagnosed my problem for back pain correctly and suggested me treatment with minimal sessions. Her treatment suited me very well as I got relief with in 2 to 3 sessions. She even took some sessions for future prevention of back pain. Her suggested Streching exercise were quite effective and easy to do at home. I would highly recommend her for any kind of Muscle pain or bad posture.
Dr Richa is a very Polite and Knowledgeable doctor. She diagnosed my problem for back pain correctly and suggested me treatment with minimal sessions. Her treatment suited me very well as I got relief with in 2 to 3 sessions. She even took some sessions for future prevention of back pain. Her suggested Streching exercise were quite effective and easy to do at home. I would highly recommend her for any kind of Muscle pain or bad posture.
 Madhavi Nibandhe2023-07-17
Madhavi Nibandhe2023-07-17 I am taking physiotherapy sessions from fitwell clinic since 4 years. Dr. Richa is highly skilled and professional. Her diagnosis and treatment is perfect. Recently Dr. RICHA is taking care of my Mother in law who is partially paralyzed. She also got her leg amputated in Aug 2022. Both Conditions (paralysis and amputation) were very critical but Dr. Richa not only took care of this but we Can see alot of development in my mother in laws Condition. She can sit independently and can stand with Lil help because of Dr. Richa. Her empathetic and loving nature helps in healing... Thank you Dr.Richa for being with us. Highly highly recommended. LOTS OF LOVE AND BEST WISHES TO YOU. MADHAVI
I am taking physiotherapy sessions from fitwell clinic since 4 years. Dr. Richa is highly skilled and professional. Her diagnosis and treatment is perfect. Recently Dr. RICHA is taking care of my Mother in law who is partially paralyzed. She also got her leg amputated in Aug 2022. Both Conditions (paralysis and amputation) were very critical but Dr. Richa not only took care of this but we Can see alot of development in my mother in laws Condition. She can sit independently and can stand with Lil help because of Dr. Richa. Her empathetic and loving nature helps in healing... Thank you Dr.Richa for being with us. Highly highly recommended. LOTS OF LOVE AND BEST WISHES TO YOU. MADHAVI
 Kalindi Dave2023-07-16
Kalindi Dave2023-07-16 This feedback goes to @Richa A BIG thank you for the wonderful care and support you gave to my father during his physiotherapy sessions. Your expertise and clear explanations were amazing in helping him understand the importance of these sessions, even though he tends to avoid visiting doctors. Having tried different physiotherapists in Kharadi, I can confidently say that I highly recommend you to anyone in need of physiotherapy. I also see you sharing valuable advice with everyone around you, addressing their mistakes and providing guidance on day-to-day posture. It's refreshing to see someone genuinely caring and offering such help without charging hefty fees. Keep up the great work! God bless you girl
This feedback goes to @Richa A BIG thank you for the wonderful care and support you gave to my father during his physiotherapy sessions. Your expertise and clear explanations were amazing in helping him understand the importance of these sessions, even though he tends to avoid visiting doctors. Having tried different physiotherapists in Kharadi, I can confidently say that I highly recommend you to anyone in need of physiotherapy. I also see you sharing valuable advice with everyone around you, addressing their mistakes and providing guidance on day-to-day posture. It's refreshing to see someone genuinely caring and offering such help without charging hefty fees. Keep up the great work! God bless you girl
Our Locations
Office No. 410, The Space, Grant Road, Kharadi, Pune - 411014
A4, Alcon Rethos, Opp. Forest County Gate #1, Kharadi, Pune 411014
Sai Nagri, Opposite New Sai Baba Temple, Chandan Nagar, Pune